created on 2013-02-03
Boids (Flock) Simulation
In the previous months, I was searching for some interesting AI algorithms to study and I’ve come across one of the coolest things I’ve ever seen in my life, Boids Simulation. Boids simulation or flock simulation is about imitating the behavior of fish schools or any other flocking animal behavior in nature.
It was first introduced by Craig Reynolds in 1986, his website is a little bit outdated but still has the best information and coolest examples.
As usual I’ve created an application, a basic model of boids simulation which consists of only 2 simple rules. Of course more rules can be added to achieve more complex behavior.
These 2 simple rules are:
1. Separation: To avoid crowding with local boids.
2. Cohesion: To move towards the average position of the local boids.
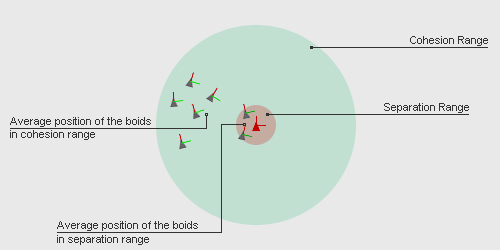
By local boids, we mean the boids in a certain range of each boid. The separation range and cohesion range are independent and can be different. In the application, cohesion range is greater than separation range and separation coefficient is greater than cohesion coefficient. This causes each boid to move as close as possible to other boids but not to collide with them.
On the top-left corner of the application, there is the user interface. With it, you can see the number of boids currently simulated, add or remove boids, make the application full-screen and control the boids’ behavior. There are 2 types of behaviors for the boids, the first and the default one is wandering behavior and the second one is following behavior. Actually, wandering behavior is also a following behavior, in wandering mode, boids follow the green circle and in following mode, they follow the mouse pointer. Red circles are obstacles, you can drag and drop them anywhere you want.
If you think that this article is wrong or missing, or maybe you have a question, please feel free to send me a message.